In today’s fast-paced digital world, understanding the sentiment score has become increasingly important. Whether you’re a business owner aiming to gauge customer satisfaction or a data analyst interpreting online trends, sentiment analysis plays a pivotal role. In this article, we will delve deep into the concept of what is sentiment score, exploring what they are, how they work, and why they matter.
What is a Sentiment Score?
A sentiment score, often referred to as a sentiment analysis score, is a numerical representation of the sentiment or emotion conveyed in a piece of text, be it a tweet, a product review, or an article. It provides insight into whether the expressed sentiment is positive, negative, or neutral. Understanding sentiment scores is essential for businesses, marketers, and data scientists, as it helps them make data-driven decisions and gain valuable insights.
How are Sentiment Scores Calculated?
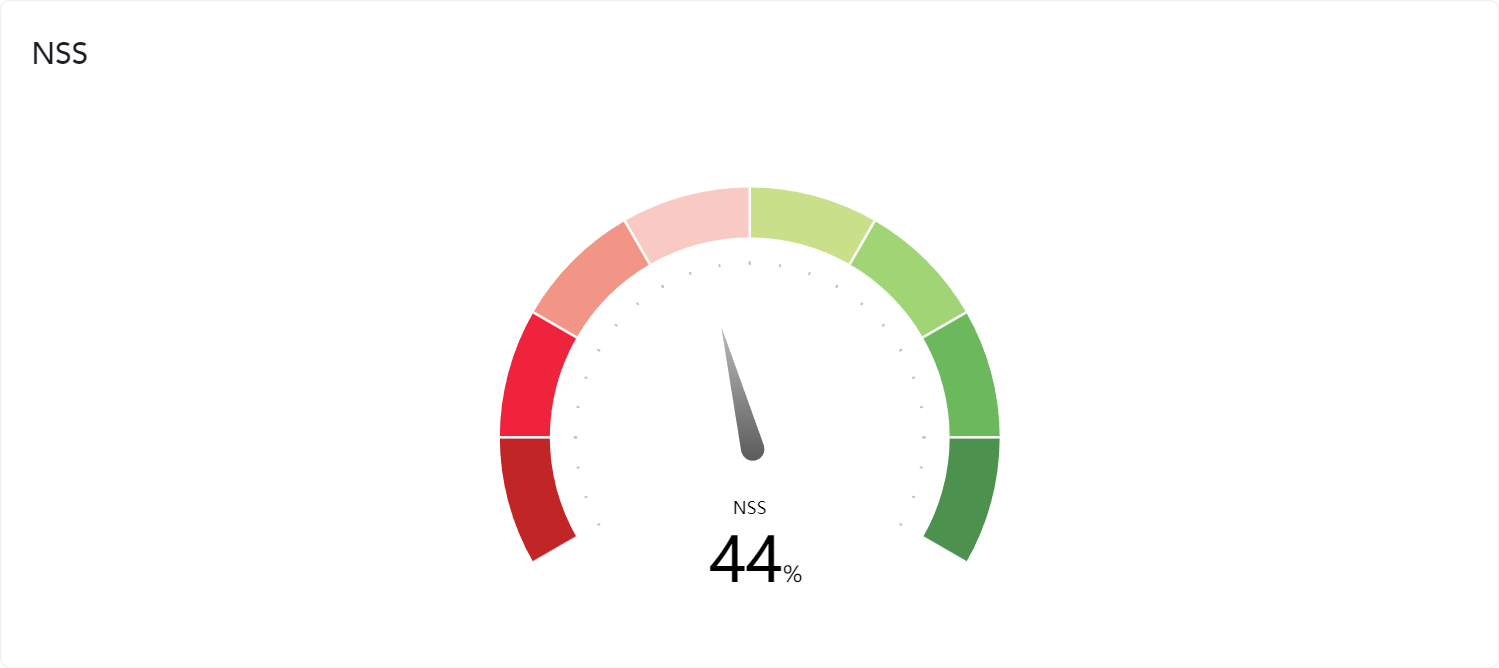
Sentiment analysis algorithms use natural language processing (NLP) techniques to determine the sentiment in text. Here’s a simplified overview of the process:
1. Text Preprocessing
Before analysis begins, the text data undergoes preprocessing. This includes tasks like removing punctuation, lowercase, and tokenization.
2. Lexicon-Based Analysis
Many sentiment analysis tools rely on lexicons or dictionaries that assign sentiment scores to words. For example, the word “happy” might have a positive score, while “sad” has a negative score.
3. Machine Learning Models
Advanced sentiment analysis employs machine learning models, such as Support Vector Machines or Recurrent Neural Networks, to analyze text and assign sentiment scores based on context and word relationships.
Applications of Sentiment Scores
Sentiment scores find applications across various fields:
1. Social Media Monitoring
Brands and marketers use sentiment analysis to monitor public perception on social media platforms. By tracking sentiment scores, they can quickly respond to customer feedback and adapt their strategies.
2. Product and Service Improvement
Understanding customer sentiment helps businesses identify areas for improvement in their products and services. Positive feedback can be reinforced, while negative feedback can guide enhancements.
3. Financial Markets
Investors and traders use sentiment analysis to gauge market sentiment, helping them make more informed decisions. Sudden shifts in sentiment can impact stock prices and other financial assets.
4. Content Creation
Content creators use sentiment analysis to tailor their content to their target audience. By understanding what resonates positively, they can craft more engaging articles, blogs, or videos.
Case Studies
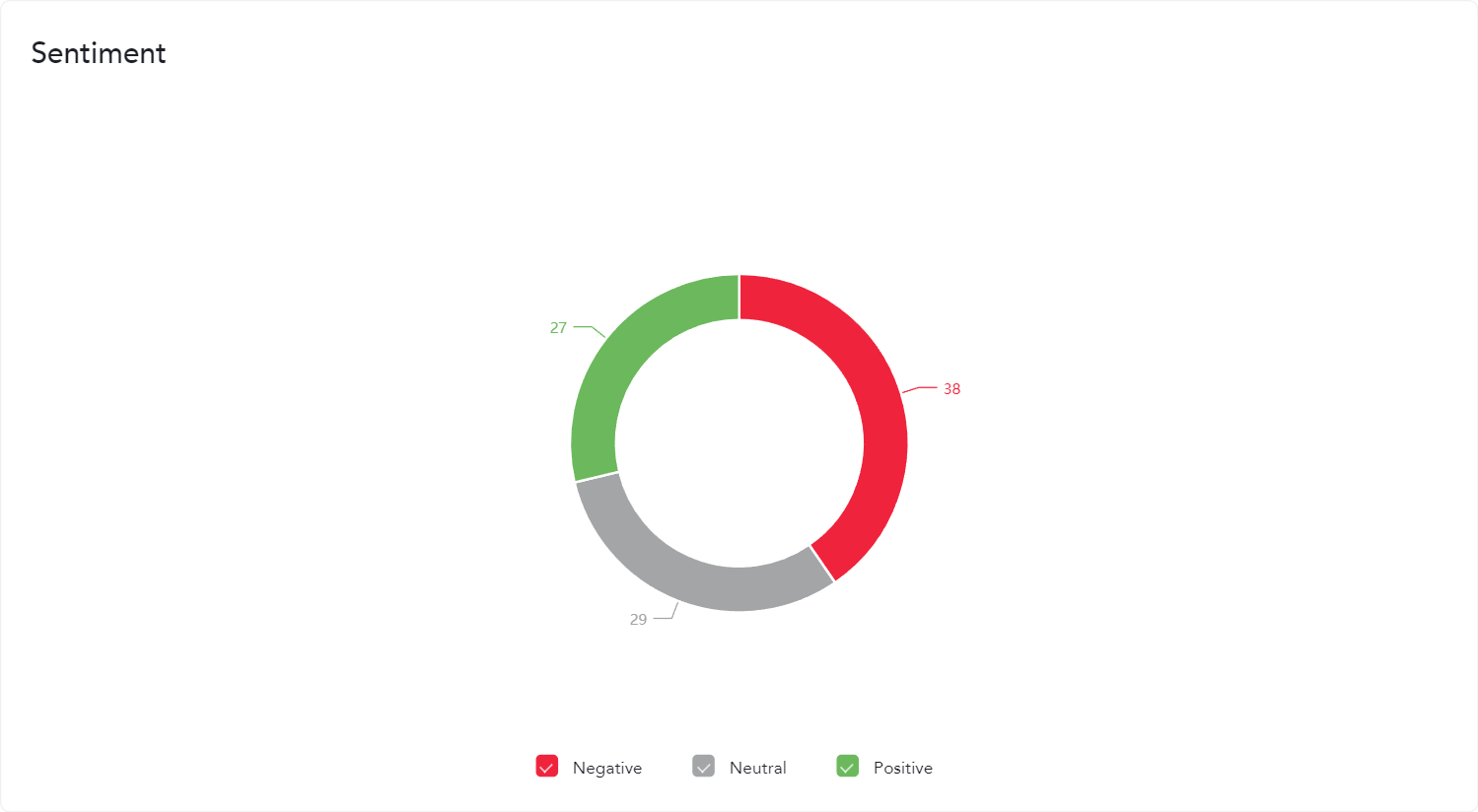
Case Study 1: Social Media Sentiment Analysis for Brand Management
A leading consumer electronics company used our sentiment analysis to monitor social media mentions of their latest product launch. By analyzing thousands of tweets and posts, they identified a growing concern about a specific feature. The company quickly addressed the issue through a public statement and a software update, mitigating potential negative impacts on its brand reputation.
Case Study 2: Sentiment Analysis in Financial Markets
A financial services firm used our sentiment analysis to predict stock price movements based on news articles and social media sentiment. By integrating sentiment scores into their trading algorithms, they achieved a 15% increase in their trading performance, demonstrating the value of sentiment analysis in financial decision-making.
Case Study 3: Improving Customer Experience in Retail
A global retail chain implemented our Arabic sentiment analysis to evaluate customer feedback from online reviews and survey responses. By identifying common pain points and areas of satisfaction, they optimized their in-store and online shopping experiences, resulting in a 20% increase in customer satisfaction scores.
Challenges in Sentiment Analysis
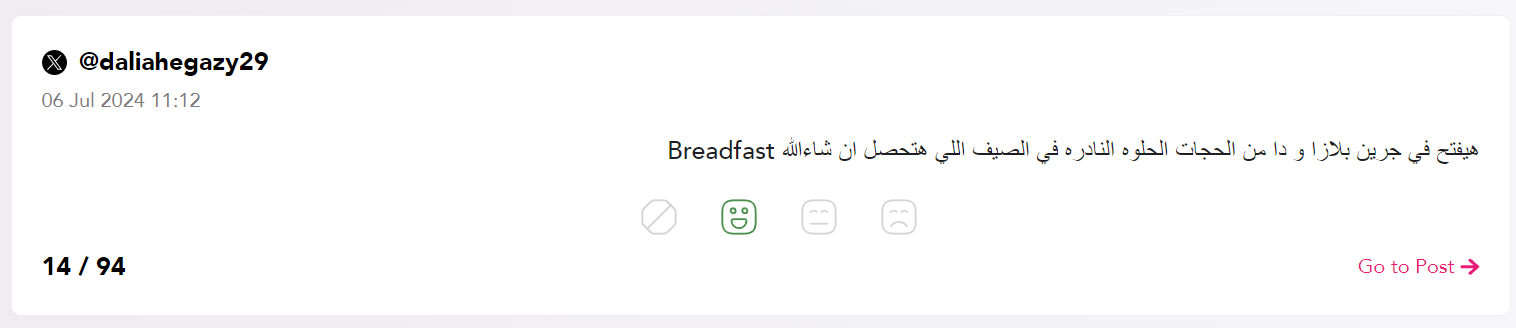
While sentiment analysis is a powerful tool, it comes with its challenges:
1. Contextual Understanding
Sentiment analysis algorithms may struggle with understanding sarcasm, irony, or context-dependent sentiment, leading to inaccuracies.
2. Multilingual Analysis
Analyzing sentiment in multiple languages can be complex due to language nuances and cultural differences.
3. Data Privacy
Privacy concerns arise when analyzing sentiment in user-generated content. Striking a balance between insights and user data protection is crucial.
Future Trends in Sentiment Score
1. Integration with Artificial Intelligence
The integration of sentiment analysis with advanced AI techniques like deep learning and reinforcement learning is expected to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of sentiment analysis tools. This will enable more nuanced understanding and better handling of complex sentiments like sarcasm and irony.
2. Multimodal Sentiment Analysis
Future sentiment analysis will increasingly consider multiple data sources, including text, audio, and video, to provide a more comprehensive understanding of sentiment. This multimodal approach will enhance the ability to analyze sentiment in real-time and in diverse contexts.
3. Sentiment Analysis in IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) will open new avenues for sentiment analysis, enabling the collection and analysis of sentiment data from smart devices and sensors. This can provide real-time insights into user experiences and preferences.
4. Personalized Sentiment Analysis
Personalized sentiment analysis will leverage individual user data to provide more tailored insights. This can help businesses understand customer preferences at a granular level, leading to more personalized marketing and customer service strategies.
5. Ethical and Transparent Sentiment Analysis
As sentiment analysis becomes more prevalent, there will be a growing emphasis on ethical considerations and transparency. Ensuring that sentiment analysis algorithms are fair, unbiased, and respect user privacy will be critical.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sentiment scores are a valuable asset in today’s data-driven world. They provide a quantitative measure of the emotions expressed in text data, enabling businesses, analysts, and individuals to make informed decisions. While challenges exist, ongoing advancements in natural language processing and machine learning promise a brighter future for sentiment analysis.
Ready to harness the power of sentiment analysis for your business? Request a demo from AIM Technologies today and discover how our cutting-edge solutions can elevate your data insights.
FAQs
1. Is sentiment analysis limited to the English language?
- No, sentiment analysis can be applied to various languages, although accuracy may vary based on language complexity and the availability of language-specific resources.
2. Are sentiment scores always accurate?
- Sentiment analysis algorithms strive for accuracy, but they may not always capture nuances, especially in complex or sarcastic text.
3. Can sentiment analysis be used for video or audio content?
- Yes, sentiment analysis can be adapted to analyze audio and video content by transcribing spoken words into text for analysis.
4. Are sentiment scores subjective?
- Sentiment scores are based on algorithms and predefined lexicons, making them objective. However, subjectivity can arise in interpreting results and context.
5. How can I start using sentiment analysis for my business?
- You can begin by exploring various sentiment analysis tools and consulting with data analysts or experts in the field to understand how they can benefit your specific business needs.


